LeetCode #21 - Merge Two Sorted Lists
November 18, 2020
Hello fellow devs 👋! It’s time to solve a new LeetCode problem.
Problem Statement
Merge two sorted linked lists and return it as a new sorted list. The new list should be made by splicing together the nodes of the first two lists.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in both lists is in the range
[0, 50]. - -100 ≤
Node.val≤ 100 - Both
l1andl2are sorted in non-decreasing order.
Examples
Example 1:
Input: l1 = [1,2,4], l2 = [1,3,4]
Output: [1,1,2,3,4,4]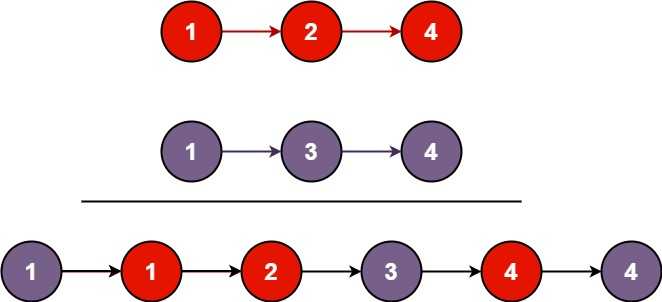
Example 2:
Input: l1 = [], l2 = []
Output: []Example 3:
Input: l1 = [], l2 = [0]
Output: [0]Analysis
We will be given two sorted linked lists, and we need to merge them in such a way that the resultant list will also be sorted. Lists are sorted in the non-decreasing order, therefore, the resultant list should also be in non-decreasing order.
Approach.
The approach is pretty straight forward. If you have worked with Merge Sort before, it is similar to that. We will use merge function of the merge sort to solve this problem. The steps are -
- Check if any of the lists is empty.
- First we need to determine the head of the resultant list. This head will be smaller of the heads of the given lists.
- Loop through each node of the lists until one of the lists get traversed completely.
- While traversing the lists, identify smaller of the nodes of the lists and add it to the resultant list.
- Once the loop is complete, there may be a case where a list has nodes remaining. We will add those remaining nodes to the resultant list.
Time Complexity
If the number of nodes are m and n in both lists, then the overall time complexity will be O(m + n) because we are traversing all the nodes of both the lists.
Space Complexity
We are creating a list to store our result, but we are not using it as part of our intermediate computations, hence the space complexity according to me will be O(1).
Code
Java
public class MergeTwoSortedLists {
private static ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
// Check if ant of the lists are null
if (l1 == null) {
return l2;
}
if (l2 == null) {
return l1;
}
// Head of the result list
ListNode head;
// Pointer for the resultant list
ListNode temp;
// Choose head which is smaller of the two lists
if (l1.val < l2.val) {
temp = head = new ListNode(l1.val);
l1 = l1.next;
} else {
temp = head = new ListNode(l2.val);
l2 = l2.next;
}
// Loop until any of the list becomes null
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
if (l1.val < l2.val) {
temp.next = new ListNode(l1.val);
l1 = l1.next;
} else {
temp.next = new ListNode(l2.val);
l2 = l2.next;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
// Add all the nodes in l1, if remaining
while (l1 != null) {
temp.next = new ListNode(l1.val);
l1 = l1.next;
temp = temp.next;
}
// Add all the nodes in l2, if remaining
while (l2 != null) {
temp.next = new ListNode(l2.val);
l2 = l2.next;
temp = temp.next;
}
return head;
}
static class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
}Python
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, nextNode=None):
self.val = val
self.next = nextNode
def mergeTwoLists(l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode) -> ListNode:
# Check if either of the lists is null
if l1 is None:
return l2
if l2 is None:
return l1
# Choose head which is smaller of the two lists
if l1.val < l2.val:
temp = head = ListNode(l1.val)
l1 = l1.next
else:
temp = head = ListNode(l2.val)
l2 = l2.next
# Loop until any of the list becomes null
while l1 is not None and l2 is not None:
if l1.val < l2.val:
temp.next = ListNode(l1.val)
l1 = l1.next
else:
temp.next = ListNode(l2.val)
l2 = l2.next
temp = temp.next
# Add all the nodes in l1, if remaining
while l1 is not None:
temp.next = ListNode(l1.val)
l1 = l1.next
temp = temp.next
# Add all the nodes in l2, if remaining
while l2 is not None:
temp.next = ListNode(l2.val)
l2 = l2.next
temp = temp.next
return headJavaScript
var mergeTwoLists = function (l1, l2) {
// Check if either of the lists is null
if (!l1) {
return l2;
}
if (!l2) {
return l1;
}
// Head of the new linked list - this is the head of the resultant list
let head = null;
// Reference of head which is null at this point
let temp = head;
// Choose head which is smaller of the two lists
if (l1.val < l2.val) {
temp = head = new ListNode(l1.val);
l1 = l1.next;
} else {
temp = head = new ListNode(l2.val);
l2 = l2.next;
}
// Loop until any of the list becomes null
while (l1 && l2) {
if (l1.val < l2.val) {
temp.next = new ListNode(l1.val);
l1 = l1.next;
temp = temp.next;
} else {
temp.next = new ListNode(l2.val);
l2 = l2.next;
temp = temp.next;
}
}
// Add all the nodes in l1, if remaining
while (l1) {
temp.next = new ListNode(l1.val);
l1 = l1.next;
temp = temp.next;
}
// Add all the nodes in l2, if remaining
while (l2) {
temp.next = new ListNode(l2.val);
l2 = l2.next;
temp = temp.next;
}
return head;
};
function ListNode(val, next) {
this.val = (val === undefined ? 0 : val)
this.next = (next === undefined ? null : next)
}Kotlin
fun mergeTwoLists(l1: ListNode?, l2: ListNode?): ListNode? {
var list1 = l1
var list2 = l2
// Check if ant of the lists are null
if (list1 == null) {
return list2
}
if (list2 == null) {
return list1
}
// Head of the result list
val head: ListNode
// Pointer for the resultant list
var temp: ListNode?
// Choose head which is smaller of the two lists
if (list1.`val` < list2.`val`) {
head = ListNode(list1.`val`)
temp = head
list1 = list1.next
} else {
head = ListNode(list2.`val`)
temp = head
list2 = list2.next
}
// Loop until any of the list becomes null
while (list1 != null && list2 != null) {
if (list1.`val` < list2.`val`) {
temp!!.next = ListNode(list1.`val`)
list1 = list1.next
} else {
temp!!.next = ListNode(list2.`val`)
list2 = list2.next
}
temp = temp.next
}
// Add all the nodes in l1, if remaining
while (list1 != null) {
temp!!.next = ListNode(list1.`val`)
list1 = list1.next
temp = temp.next
}
// Add all the nodes in l2, if remaining
while (list2 != null) {
temp!!.next = ListNode(list2.`val`)
list2 = list2.next
temp = temp.next
}
return head
}
class ListNode(var `val`: Int) {
var next: ListNode? = null
}Complete Code
Conclusion
Congratulations 👏! We have solved the problem using merge function of merge sort.
I hope you enjoyed this post. Feel free to share your thoughts on this.
You can find the complete source code on my GitHub repository. If you like what you learn, feel free to fork 🔪 and star ⭐ it.
Till next time… Happy coding 😄 and Namaste 🙏!
