LeetCode #24 - Swap Nodes In Pairs
December 08, 2020
Hello fellow devs 👋! In this post, we will discuss another linked list problem.
Problem Statement
Given a linked list, swap every two adjacent nodes and return its head. You may not modify the values in the list’s nodes. Only nodes itself may be changed.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range [0, 100].
- 0 ≤
Node.val≤ 100
Examples
Example 1:
Input: head = [1,2,3,4]
Output: [2,1,4,3]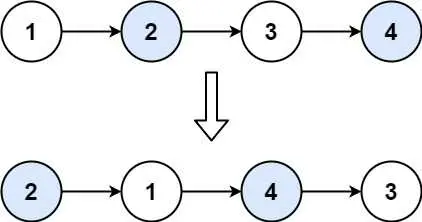
Example 2:
Input: head = []
Output: []Example 3:
Input: head = [1]
Output: [1]Analysis
We are given a linked list and we need to swap nodes in pairs. What this means is that at a time we take two nodes and swap them, then take next two nodes and then swap them. This will go on until all the nodes are left.
The constraint is that we cannot update the data in the nodes. We can only change the node pointers appropriately to solve this problem.
Approach
We can follow below steps —
- Create a
dummynode whose next pointer will point to the current head. - Now take a
currentnode which will be used to traverse the list - In each iteration, take two nodes,
first = current.nextandsecond = current.next.next. - Point the next of
firstto the next ofsecondwhich is actually the thirst node from the current. - Link the pointers accordingly and at last return the
dummy.next.
Time Complexity
Since we are traversing all the nodes of the linked list, the time complexity will be O(n).
Space Complexity
Since we are not using any data structure for intermediate computations, therefore, the space complexity will be O(1).
Code
Java
public class SwapNodesInPairs {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
// Dummy node
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
// Point the next of dummy node to the head
dummy.next = head;
// This node will be used to traverse the list
ListNode current = dummy;
// Loop until we reach to the second last node
while (current.next != null && current.next.next != null) {
// First node of the pair
ListNode first = current.next;
// Second node of the pair
ListNode second = current.next.next;
// Point the next of first node to the node after second node
first.next = second.next;
// Now the current node's next should be the second node
current.next = second;
// Linking the original second node to the first node
current.next.next = first;
// Move the pointer two nodes ahead
current = current.next.next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}Python
class SwapNodesInPairs:
def swapPairs(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
# Dummy node
dummy = ListNode(0)
# Point the next of dummy node to the head
dummy.next = head
# This node will be used to traverse the list
current = dummy
# Loop until we reach to the second last node
while current.next is not None and current.next.next is not None:
# First node of the pair
first = current.next
# Second node of the pair
second = current.next.next
# Point the next of first node to the node after second node
first.next = second.next
# Now the current node's next should be the second node
current.next = second
# Linking the original second node to the first node
current.next.next = first
# Move the pointer two nodes ahead
current = current.next.next
return dummy.nextJavaScript
var swapPairs = function (head) {
// Dummy node
const dummy = new ListNode(0);
// Point the next of dummy node to the head
dummy.next = head;
// This node will be used to traverse the list
let current = dummy;
// Loop until we reach to the second last node
while (current.next !== null && current.next !== undefined && current.next.next !== null) {
// First node of the pair
let first = current.next;
// Second node of the pair
let second = current.next.next;
// Point the next of first node to the node after second node
first.next = second.next;
// Now the current node's next should be the second node
current.next = second;
// Linking the original second node to the first node
current.next.next = first;
// Move the pointer two nodes ahead
current = current.next.next;
}
return dummy.next;
};Kotlin
class SwapNodesInPairs {
fun swapPairs(head: ListNode?): ListNode? {
// Dummy node
val dummy = ListNode(0)
// Point the next of dummy node to the head
dummy.next = head
// This node will be used to traverse the list
var current: ListNode? = dummy
// Loop until we reach to the second last node
while (current!!.next != null && current.next!!.next != null) {
// First node of the pair
val first = current.next
// Second node of the pair
val second = current.next!!.next
// Point the next of first node to the node after second node
first!!.next = second!!.next
// Now the current node's next should be the second node
current.next = second
// Linking the original second node to the first node
current.next!!.next = first
// Move the pointer two nodes ahead
current = current.next!!.next
}
return dummy.next
}
}Complete Code
Conclusion
Congratulations 👏! We have solved another linked list problem.
I hope you enjoyed this post. Feel free to share your thoughts on this.
You can find the complete source code on my GitHub repository. If you like what you learn, feel free to fork 🔪 and star ⭐ it.
Till next time… Happy coding 😄 and Namaste 🙏!
